
Governing usually has two bearers: The sovereign owner (the one who has conquered the land and has no immediate connection with the land itself) and the user (the one who is working the land – the vassal). In return, the senior is obligated to aid the vassal. According to this agreement, the vassal is obligated to consilium – attending the meeting which the senior calls, and auxilium – which is aid (financial or military). The senior and the vassal are connected by a vassal agreement. The Vassal is a freeman who is willingly engaging in a personal relationship with another freeman, the senior.
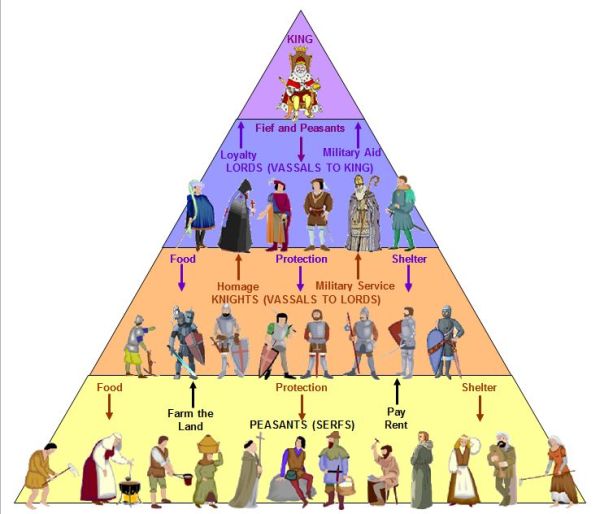
The development of European feudalism begins in the 8th century, the time of the first Merovingians and Carolingians, with the interconnection of the granting of fiefs and the establishing of personal vassal-senior relations. The “feudal society” mostly developed in a autarchic (independent) agricultural economy, this way of development is characteristic for societies such as these, where agriculture is the dominant branch of economic gain. In a broader sense, this term encompasses “feudal society”, as a system of economic, social and political organization that is founded on the relationship of individuals, in which one class of specialized warriors – feudal lords – which are ranked in a strict hierarchy of intertwined dependencies, rules over a mass of peasants who work the land and provide for their living. Feudalism, in a stricter sense, represents a system of rights and obligations that is founded on the ownership of land, and the personal relations in which the vassals hold fiefs (land) that is granted by their lord (senior).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
